Abstract
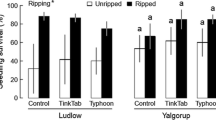
To identify potential constraints on willow (Salix spp.) seedling establishment in montane riparian communities in Rocky Mountain National Park, Colorado, USA we established a controlled experiment to examine the effects of soil texture and elevation above river stage on willow seedling survival. We followed seedling survival rates over two summers in paired course- and fine-textured plots established at three elevations on study area point bars. Patterns of seedling survival changed over the course of the study, and after two growing seasons, greater seedling survival rates were observed in fine-textured plots and plots occuring at high and intermediate elevations. Our results indicate that both soil water availability and scour by spring floods influence the spatial and temporal patterns of willow seedling survival on point bars along small-order montane streams.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Adair, E. C. and D. Binkley. 2002. Co-limitation of first year Fremont cottonwood seedlings by nitrogen and water. Wetlands 22: 425–429.
Alstad, K. P., J. M. Walker, S. A. Williams, and M. J. Trlica. 1999. Carbon and water relations of Salix monticola in response to winter browsing and changes in surface water hydrology: an isotopic study using δ13C and δ13O. Oecologia 120:375–385.
Amlin, N. M. and S. B. Rood. 2002. Comparative tolerances of riparian willows and cottonwoods to water-table decline. Wetlands 22:338–346.
Baker, W. L. 1990. Climatic and hydrologic effects on the regeneration of Populus angustifolia James along the Animas River, Colorado. Journal of Biogeography 17:59–73.
Busch, D. E., N. L. Ingraham, and S. D. Smith. 1992. Water-uptake in woody riparian phreatophytes of the southwestern United-States—a stable isotope study. Ecological Applications 2:450–459.
Cooper, D. J., D. M. Merritt, D. C. Anderson, and R. A. Chimner. 1999. Factors controlling the establishment of Fremont cottonwood seedlings on the upper Green River, USA. Regulated Rivers: Research and Management 15:419–440.
Dixon, M. D., M. G. Turner, and C. F. Jin. 2002. Riparian tree seedling distribution on Wisconsin River sandbars: controls at different spatial scales. Ecological Monographs 72:465–485.
Dixon, M. D. 2003. Effects of flow pattern on riparian seedling recruitment on sandbars in the Wisconsin River, Wisconsin, USA. Wetlands 23:125–139.
Ellenberg, H. 1998. Vegetation Ecology of Central Europe. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Johnson, W. C. 2000. Tree recruitment and survival in rivers: influence of hydrological processes. Hydrological Processes 14:3051–3074.
Karrenberg, S., P. J. Edwards, and J. Kollmann. 2002. The life history of Salicaceae living in the active zone of floodplains. Freshwater Biology 47:733–748.
Levine, C. M. and J. C. Stromberg. 2001. Effects of flooding on native and exotic plant seedlings: implications for restoring southwestern riparian forests by manipulating water and sediment flows. Journal of Arid Environments 49:111–131.
Mahoney, J. M. and S. B. Rood. 1998. Streamflow requirements for cottonwood seedling recruitment—an integrative model. Wetlands 18:634–645.
McBride, J. R. and J. Strahan. 1984. Establishment and survival of woody riparian species on gravel bars of an intermittent stream. The American Midland Naturalist 12:235–245.
Meentemeyer, R. K. and D. R. Butler. 1999. Hydrogeomorphic effects of beaver dams in Glacier National Park, Montana. Physical Geography 20:436–446.
Moss, E. H. 1938. Longevity of seed and establishment of seedlings in species of Populus. Botanical Gazette 99:529–542.
Patten, D. T. 1998. Riparian ecosystems of semi-arid North America: diversity and human impacts. Wetlands 18:498–512.
Peinetti, H. R., M. A. Kalkhan, and M. B. Coughenour. 2002. Longterm changes in willow spatial distribution on the elk winter range of Rocky Mountain National Park (USA). Landscape Ecology 17: 341–354.
Sacchi, C. F. and P. W. Price. 1992. The relative roles of abiotic and biotic factors in seedling demography of arroyo willow (Salix lasiolepis: Salicaceae). American Journal of Botany 79:395–405.
Scott, M. L., J. M. Friedman, and G. T. Auble. 1996. Fluvial process and the establishment of bottomland trees. Geomorphology 14: 327–339.
Scott, M. L., G. T. Auble, and J. M. Friedman. 1997. Flood dependency of cottonwood establishment along the Missouri River, Montana, USA. Ecological Applications 7:677–690.
Woods, S. W. 2001. Ecohydrology of subalpine wetlands in the Kawuneeche Valley, Rocky Mountain National Park, Colorado. Ph.D. Dissertation. Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gage, E.A., Cooper, D.J. Constraints on willow seedling survival in a Rocky Mountain Montane floodplain. Wetlands 24, 908–911 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2004)024[0908:COWSSI]2.0.CO;2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2004)024[0908:COWSSI]2.0.CO;2